What are the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders?
Identifying the key stakeholders (along with their roles, responsibilities, and interests in the project) will help you communicate and work with them more efficiently. The goal is to identify and satisfy their needs and achieve the project requirements successfully.
The chart below is an example of the composition of a project team at SSU. The chart is followed by a table that describes the general role and responsibilities for each of these stakeholders.
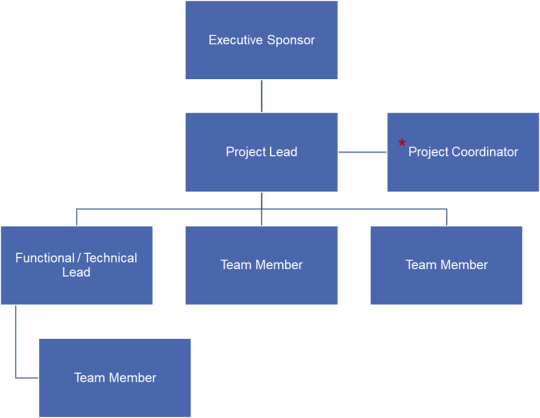
*Project Coordinators are allocated depending on the project’s characteristics. In projects with no Project Coordinators, the IT Project Lead will perform the project coordination activities.
The following roles and responsibilities are generic descriptions and these can be modified and tailored according to the specific needs of each project. For instance, a team member can be a subject matter expert in software development and hence his/her responsibilities will need to be adjusted to describe the specific activities that they will be executing as part of their role in the project. The Project Charter must include the list of stakeholders as well as their roles and responsibilities in the project.
| Project Role | Responsibilities | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Executive Sponsor |
A person or group who provides resources and support for the project and is accountable for enabling success. |
Help eliminate barriers. Approves final plan. |
|
Project Lead |
Main person accountable for the success of the project. Work plan, resources allocation, risk management, scope change control, milestones monitoring, and communicates project status to all stakeholders. |
Authority to manage people, conflict, risks and issues. If not an MPP, seek authority from supervisor. |
|
Project Coordinator |
Coordinates project effort from start to end. Applies project management methodologies and tools to ensure projects deliver the expected results within scope, time, and budget. |
Limited authority over resources. Escalates risks, issues, and people management matters to the Project Lead. |
|
Functional / Technical Lead |
SME responsible for leading the effort of a functional or technical area (e.g. CMS, CO, Networking, etc.) |
Authority to assign work and resources. |
|
Team Member (Subject Matter Experts - SMEs) |
Staff members who exhibit high level of expertise in a specialized job, task, or skill. SMEs are responsible for performing specific tasks of the project to achieve its objectives (e.g. Sysadmin, Web Developer, Business Analyst, etc.). They help defining requirements and are often heavily involved in testing and training. |
They report progress of their work, and related issues or risks to the Project Lead and Project Coordinator. |

